-
 Mei Zhang
Booking.com
Senior Product Designer
Mei Zhang
Booking.com
Senior Product Designer
Current senior product designer at Booking.com, leading property booking and user generated content businesses, dedicated to providing travelers worldwide with smooth travel experiences. I am passionate about unifying design through streamlined collaboration, ultimately amplifying benefits for both customers and the business. Within Booking.com, I have led community projects as well to improve design quality and influence.
Design philosophy: The most fulfilling part of UX design is to discover the sweet spot between user needs and business goals. Good design should be user-centered while also supporting business.
Design Influence: Designing a Product Vision with Stakeholders and Enhancing Travel Experience
To bring good user experience to users, designers need to not only hone their design capabilities, but also be able to influence product decisions and create value for users. How to increase the influence of a designer on a team? In addition to linking day-to-day output to business goals, designers should have the power to, for example, work with senior decision makers to map out the product vision for the next five years to ensure that the product is strategically user-centric.
This workshop is based on the framework of product vision production, touching on multiple dimensions of design influence: decision-makers' managerial competence, business competence, organizational competence, and the ability to speak with data. I will combine specific cases to show the skills needed in each link of the product vision from 0 to 1. Workshop participants will also practice each knowledge point in the process of making the vision.
The main contents of this workshop:
1. Background introduction: The need to design the significance of influence
1.1 Influence: Who is affected and what is our goal?
1.2 Dimensions of influence, positive and negative cases, problem discovery and communication, business thinking, data analysis, workplace emotional intelligence, organization of teammates, etc
2. Introduce the "Product Vision Framework" : Effectively work with decision makers to develop product strategies of value to users
· Basic process of the Product Vision Framework, case study: travel product comparison
2.1 Step 1: Identify the partner, time frame and business questions that need to be answered
2.2 Step 2: Through user survey, data analysis, user journey chart, technical framework and main business indicators, understand the current performance of the product and main user pain points
2.3 The third step: prioritize user pain points, grasp five major user needs combined with the company's product strategy and propose solutions, verify the solutions proposed in the third step through user research and quantitative testing, and conduct iterative analysis
2.4 Step 4: Design sprint, string the iterative scheme into a user story and make a speech
2.5 Step 5: How to implement the design, prioritize the design with the product manager and plan it into the team development
3. Summary and review: Methods to expand influence in the process of self-creation
3.1 The essence of product vision lies in cooperation and unity
3.2 Know your Partner: Analyze each decision maker
3.3 Collaborate and connect with other projects to increase priority
3.4 Strike a balance between users and businesses: Design solutions to make them more user-friendly
1、Workshop introduction, ice-breaking and content summary
2、Explain the concept of design influence, combine with specific cases and disassemble from five dimensions
3、Design Case: Booking.com Traveler Planning and Design Vision Process
4、Site proposition: Under the setting of tourism products, make new design vision in groups to practice the newly learned knowledge, and role-play different decision makers and designers
5、Summary and review
6、Free question and answer sessions
1、Junior Designer/Product Manager
2、People who want to increase the impact of design
3、People who are interested in foreign Internet company culture
1、What is design impact and why is it important
2、How to expand design influence and voice by working with decision makers to create product vision
3、Understand foreign design culture and cooperation methods in work
-
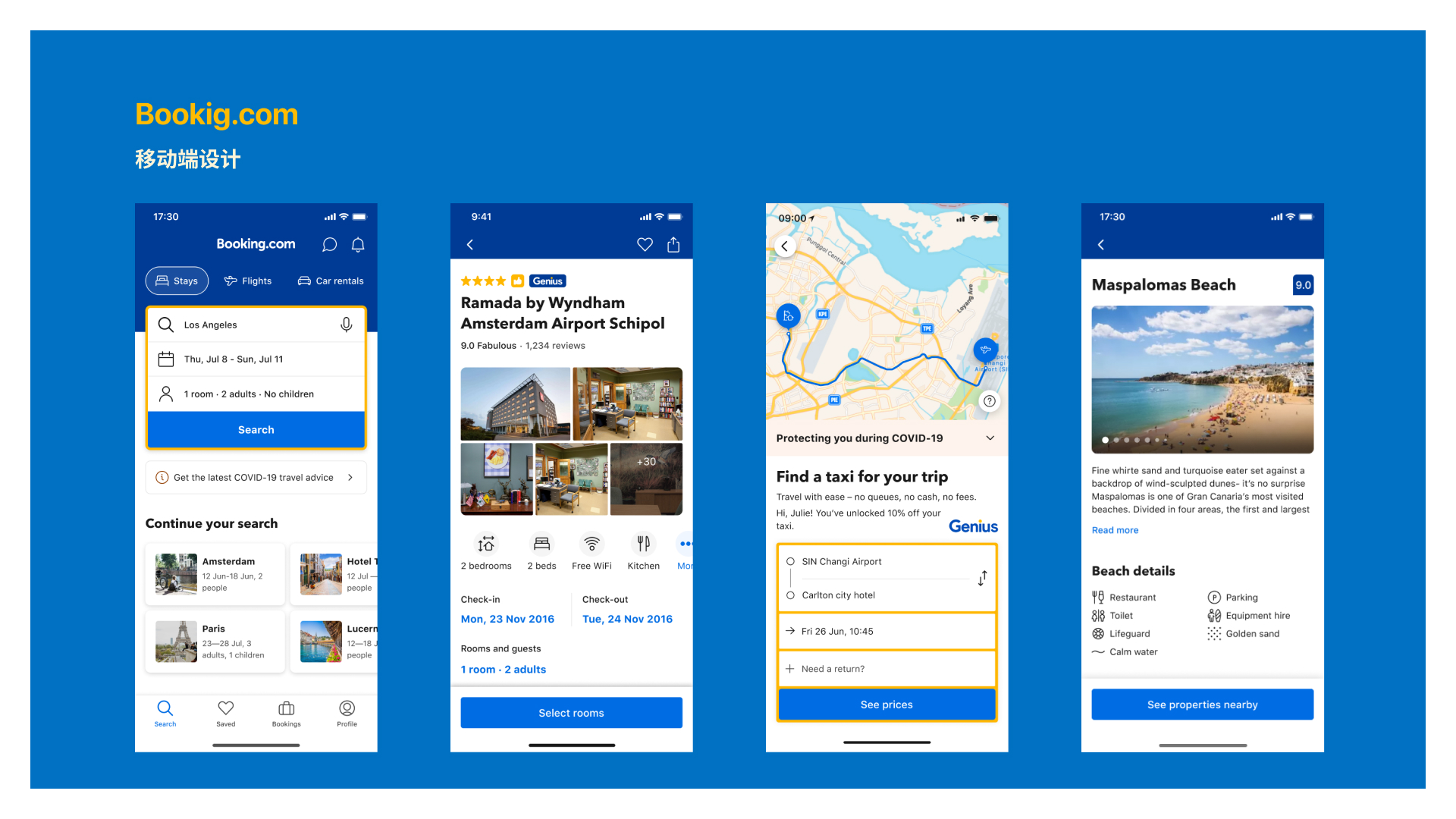 Mobile app design
Mobile app design
-
 Design influence
Design influence
-
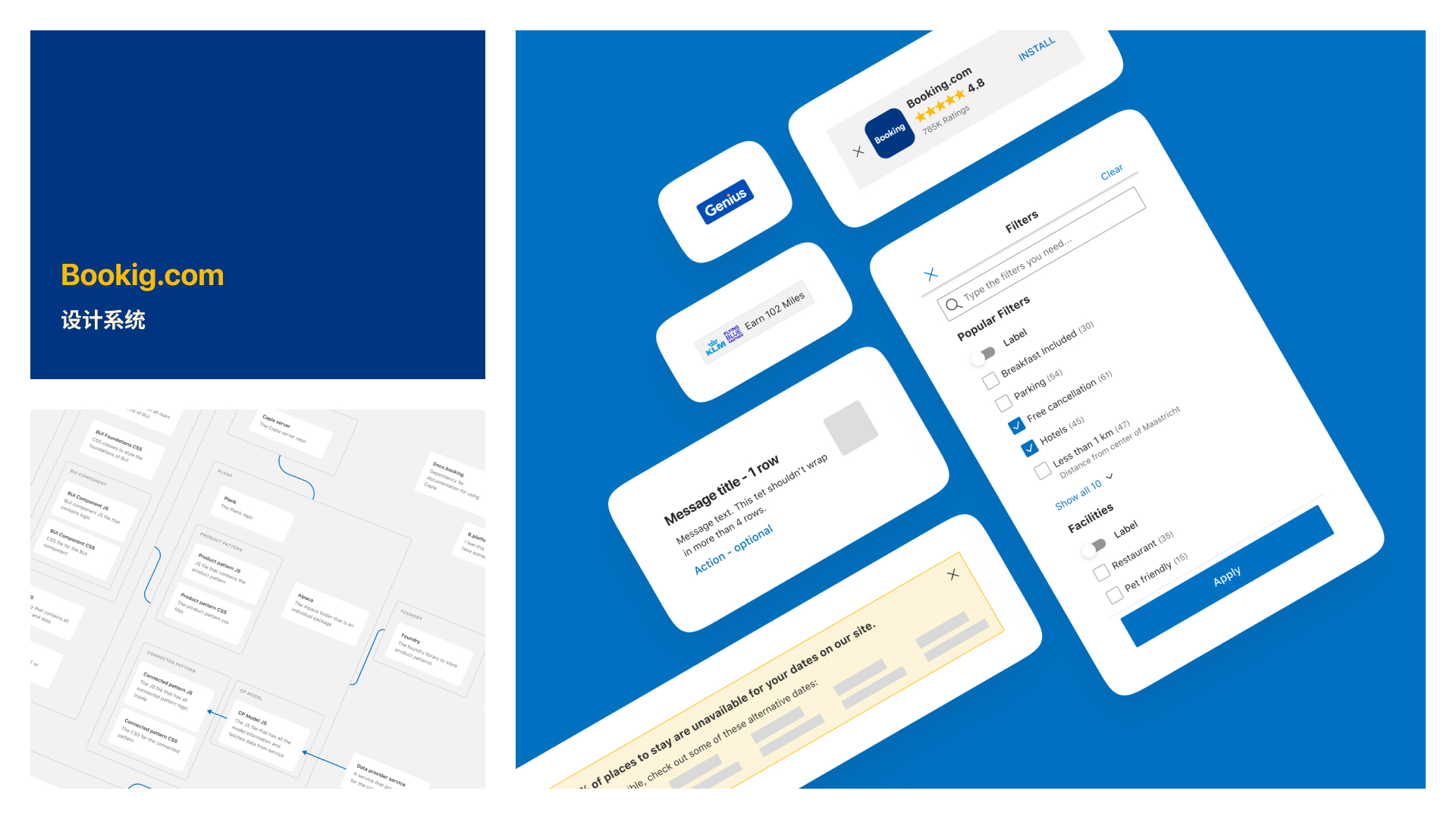 Design system
Design system
-
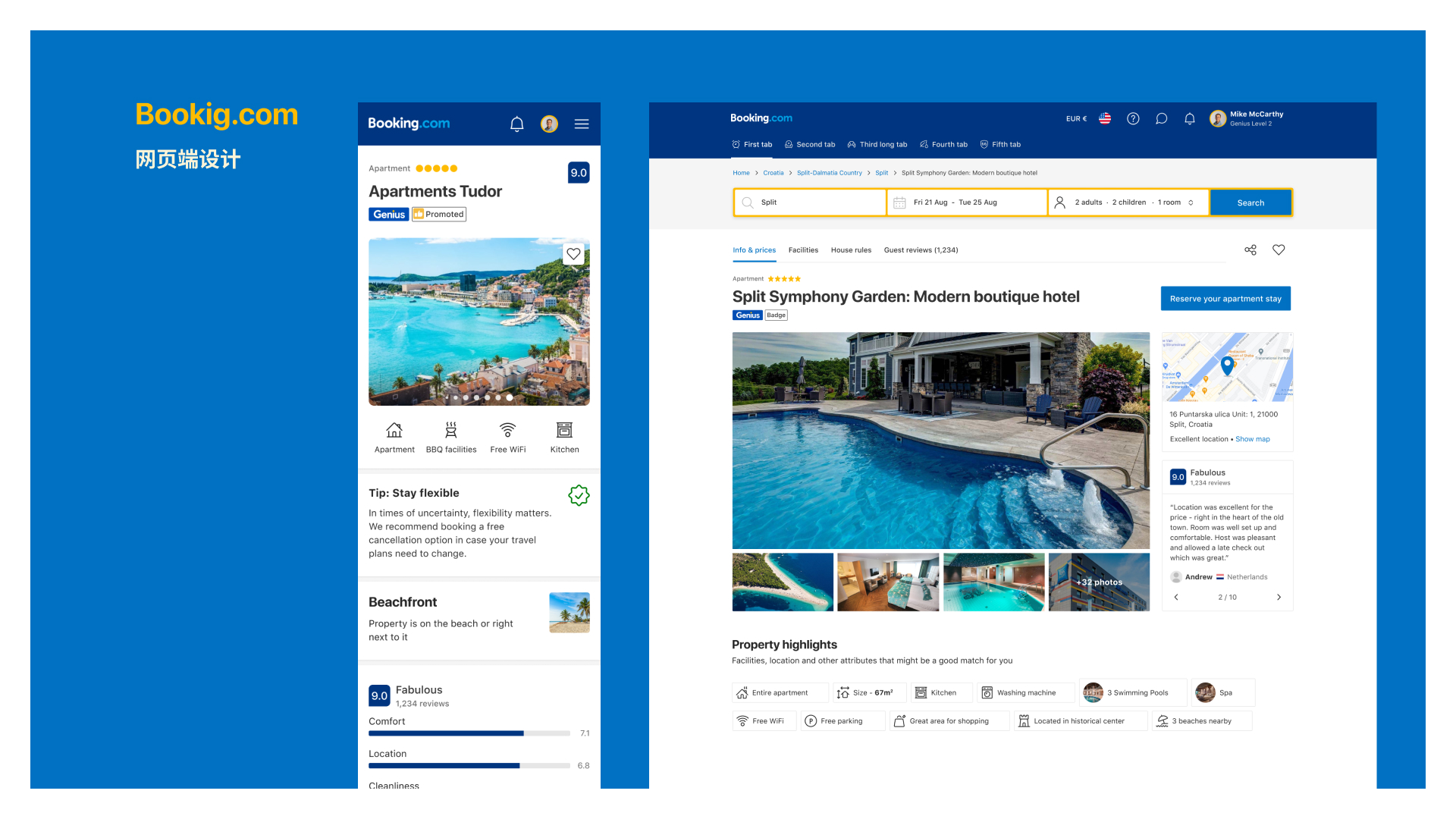 Web design
Web design
-
 Product vision roadmap
Product vision roadmap
-
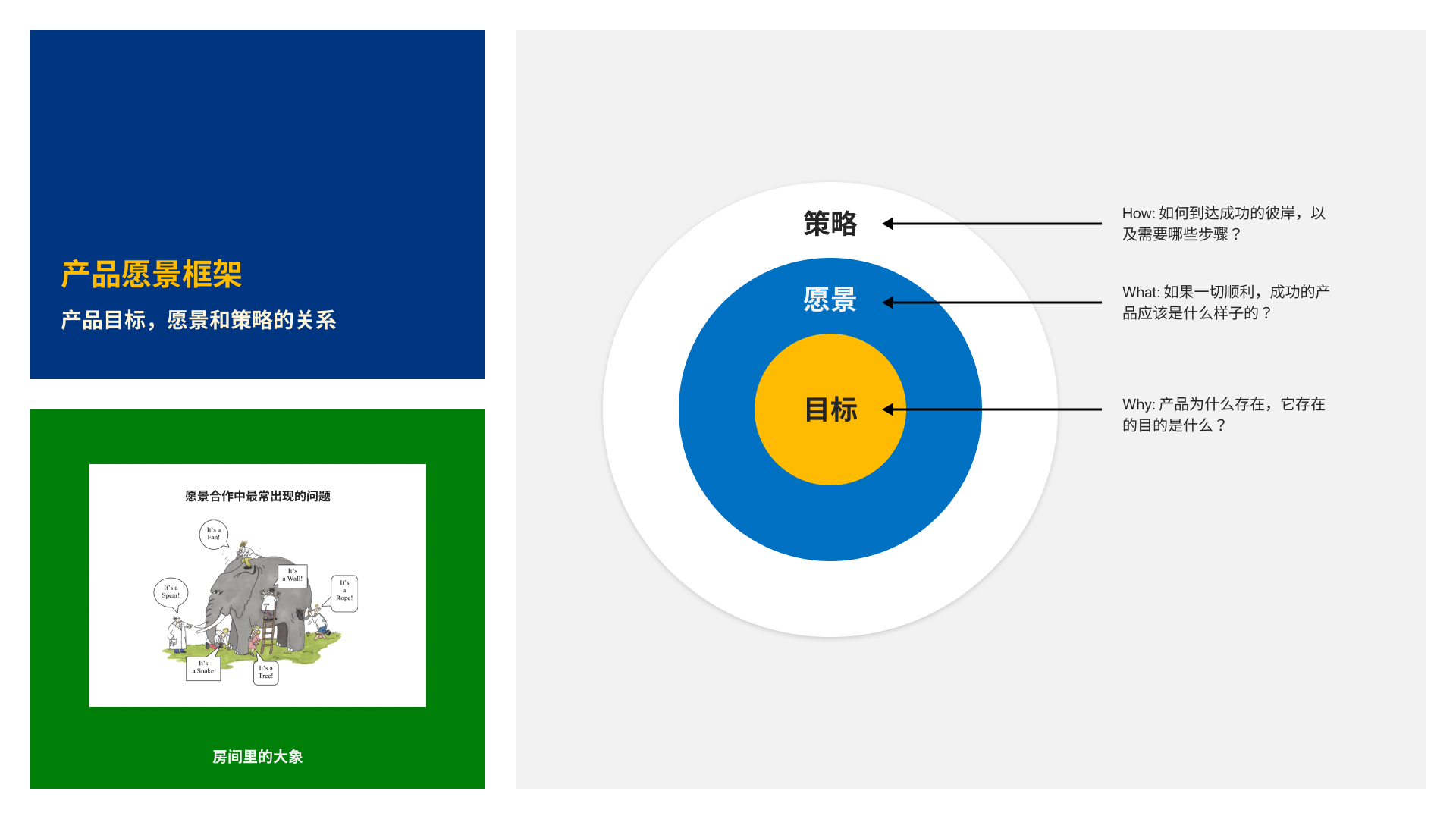 Product vision framework
Product vision framework








